Arcane University:NetImmerse Format/BSLightingShaderProperty
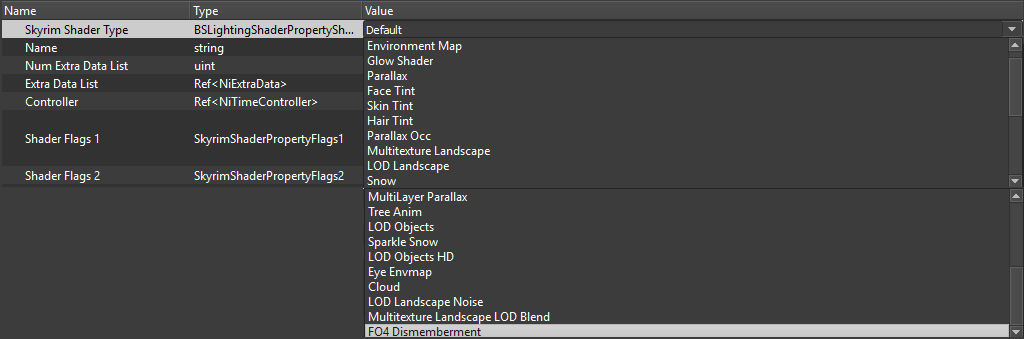
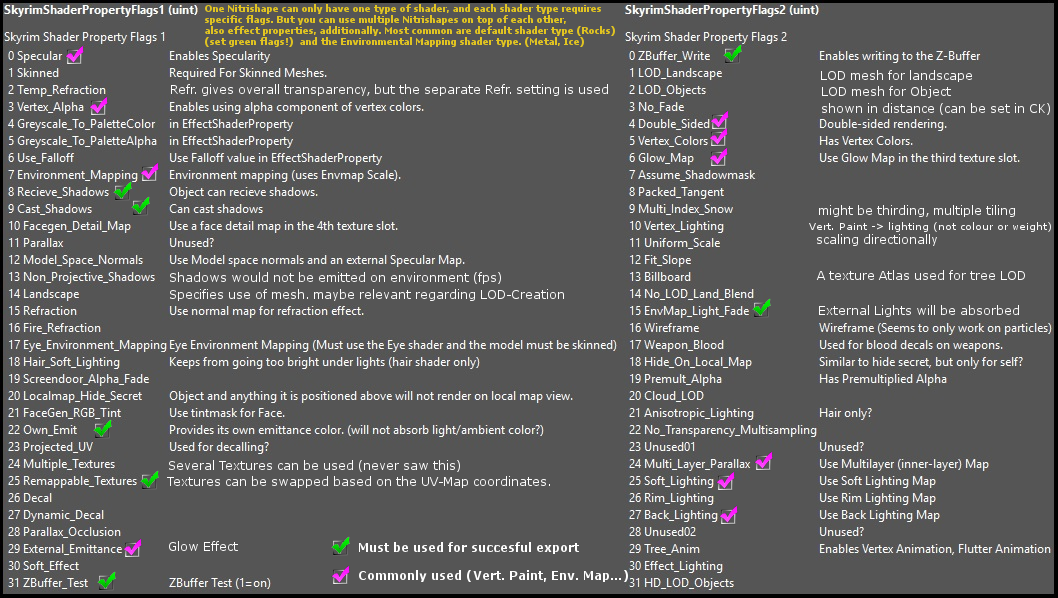
Here you can see the available shader types of a BSLightingShaderProperty. They also need specific shader flags to be set and specific texture maps. Some are essential, others optional. These are all the available Shader Flags for Skyrim:
Commonly used in Skyrim are Default shader type (“0”) and Environment Map shader type (“1”). Green shows you those who are essential for exporting a default type mesh successfully, the minimum to be set. Pink are those commonly used additional options for Lighting, environment mapping, or weighting (rigging), glow effects. There are more advanced features like multilayer parallax, but the intention of this short tutorial is, to give people a quick and solid introduction into the rendering settings for meshes used in Skyrim, which are unlike the more recent PBR Systems. You set your mesh shader property type in BSLightingShaderProperties. Note that each NiTriShape can only have one shader type and a small range of optional shader flags and use specific controllers (properties seen below).
- The standard for the Glossiness value is 100. It ranged between 0 and 999.
- Specular Strength ranges from 0 to 10 but 2 would already be very strong, 1 being the default.
- Refraction Strength ranges from 0 to 1. 1 being absolute transparency.
- Alpha also does transparency but in a different way.
- Emissive Colour and Specular Colour are the RGB values that are shining or reflecting when looking straight at the mesh.
- UV Scale is the scaling size of the UV map. You can right-click on your mesh in the render window and chose textures / UV map and manually edit it, rotate, and scale it.
The most commonly used BSLightingShaderProperties are Default shader type (“0”) and Environment Map shader type (“1”). You set your mesh shader property type in BSLightingShaderProperties. Note that each NiTriShape can only have one shader type and a small range of optional shader flags and use specific controllers(see below). But, if needed, you can simply use multiple NiTriShapes combined on top of each other. As an example, it might make sense to split your mesh into subsections by material (metal, leather) and export each as a different NiTriShape (first sublevel) into the same mesh. Consider a leather armor for instance. I would suggest having an organic leather/cloth part (which usually absorbs light to a high degree and would use the default shader type) and the metal elements (which would reflect light stronger and profit from cube maps used in the environment map shader type).
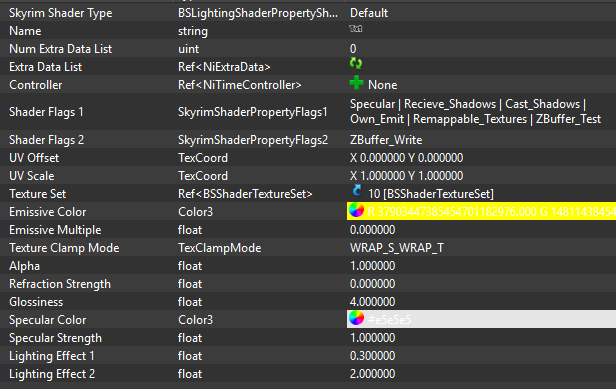
Default Shader
- Name: Default Shader Type (0)
- used for: Assets with color, height, and specularity.
- common examples: rocks, clothes, furniture, stones, plants, sometimes metals if specularity is done in a way that can pretend metallic reflections.
- necessary slots: Slot1) base color/diffuse map AND Slot2) normal map with specularity in alpha channel (optional)
- necessary flags: those who are marked green above under shader flags, for export; and additionally what you need (vertex paint, specularity for example, if you learned how to apply these)
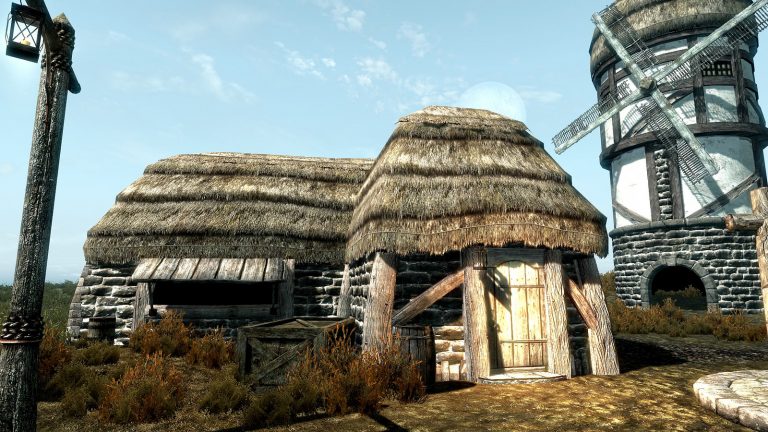
A House as an example and the shader flags and lighting properties.
The texture set of a default shader set, consisting of a diffuse and normal map.
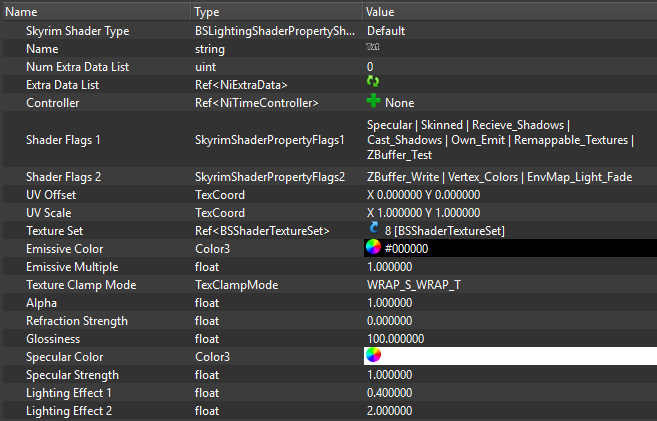
Environmental Shader
- Name: Environment Map Shader Type (1)
- used for: Assets with colour, height, and specularity and additional shininess or gloss.
- common examples: Metals, Chitin, Ore, Armours, Glass, Mirrors, Ice (more stable and consistent with ENBs than parallax)
- necessary slots: Slot 1) base color/diffuse map AND Slot 2) normal map with specularity in alpha channel (optional) AND environmental/cube map (slot 5) (DTX1, see DDS Texture files for details) AND optional: an environment mask (_m or _em), that sets which areas are reflective (Slot 6)
- necessary flags: SLSF1_Environment_Mapping, SLSF2_Glow_Map disabled
- controllers: Environmental Map Scale; 1 is normal intensity, less is lower intensity, greater is higher intensity.
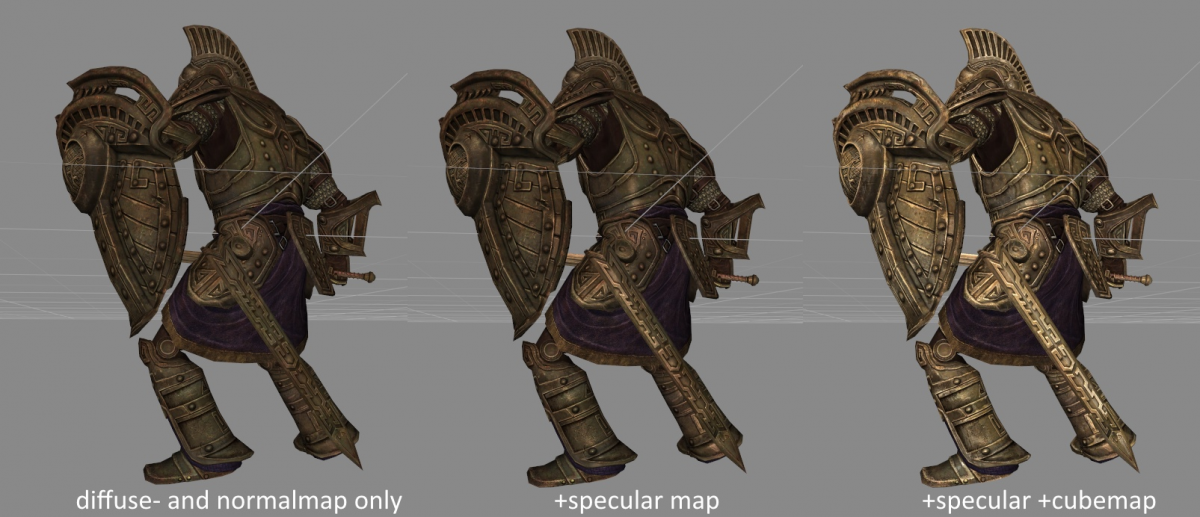
Dwemer armour only with slot 1 and slot 2 (diffuse and normal); Dwemer armour with additional m map in slot 6; Dwemer armour with additional cube map on top of that in slot 5.
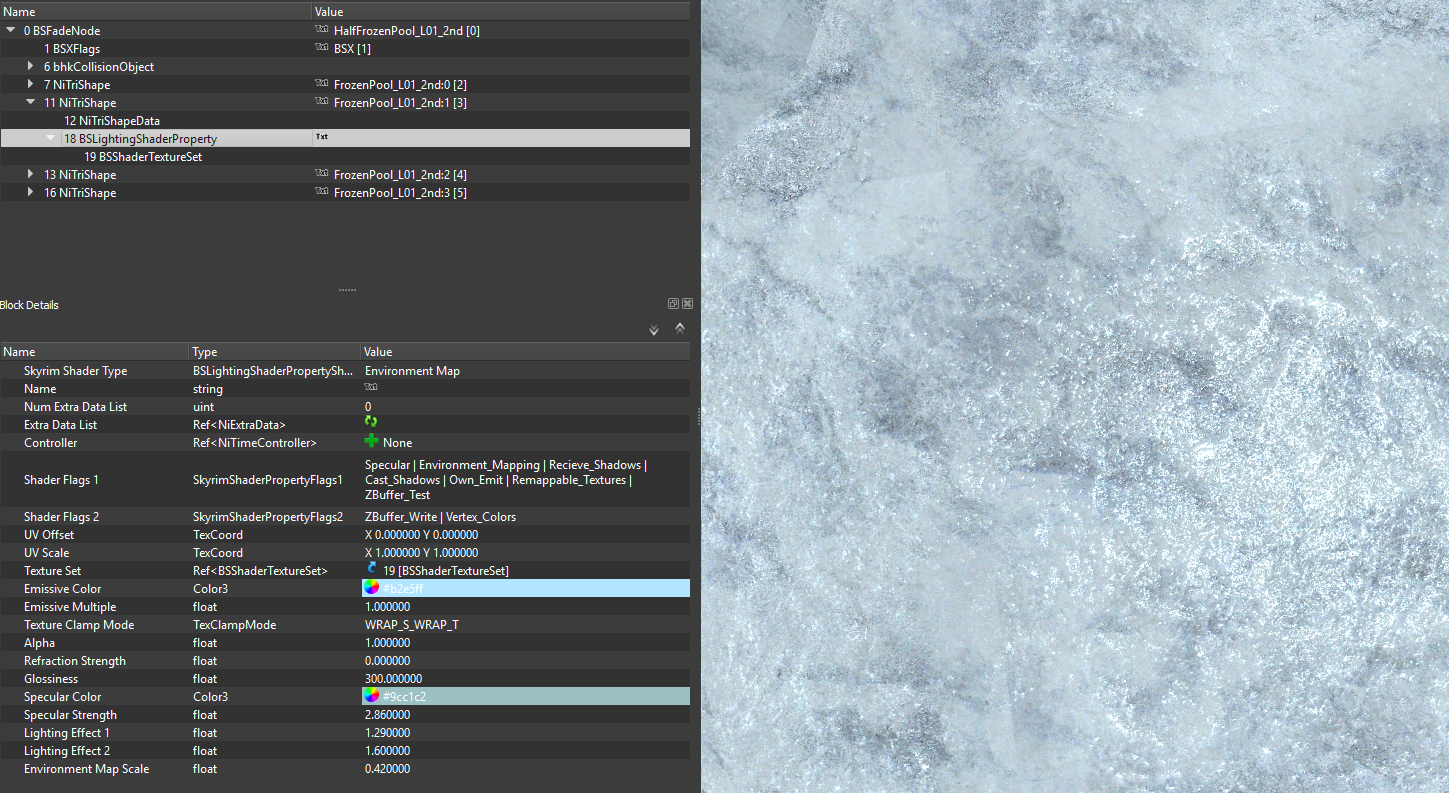
Ice: Example of BSLightingshaderproperties controller settings. The ice profits from a detailed normal map with a spec map and the resulting specularity and gloss can be set only by these. An ice cubemap is used in slot 5, but no material map in slot 6.
A typical metal texture set for Skyrim: the rendering will make the diffuse appear much brighter. A lot of detail is being baked into the diffuse. Finally, the sword appears silver-metallic in the game engine.
For how to work on the material map for the roughness and metallic shine, see https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DWs9rDpA5tQ