Difference between revisions of "Arcane University:NetImmerse Format/BSLightingShaderProperty"
(move from nif page) |
(rewrite. wip) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | {{Trail|Nif implementation}} |
| + | The '''BSLightingShaderProperty''' is the most common type of [[AU:NetImmerse Format#Shader properties|shader property]] used in Skyrim. It defines the attributes of the material which is used for shading the mesh. It is suitable for most tangible objects. For objects which require more elaborate blending effects, a [[AU:NetImmerse Format/BSEffectShaderProperty|BSEffectShaderProperty]] may be better. | ||
| − | + | == Shader Types == | |
| + | There are several overall shader types which you can choose from. They are ordered here and in NifSkope generally from most common to least common. Each one uses the textures in its child block BSTextureSet slightly differently. Some of the data which is used in common across different shader types is outlined below: | ||
| − | + | * '''Glossiness''': Inverse width of the specular highlight. Higher values are narrower, lower values are wider. | |
| + | * '''Specular Color''': The color of the specular highlight. | ||
| + | * '''Specular Strength''': Multiplier on specular highlight intensity. Values between 0.25 and 1 are typical. | ||
| + | * '''Refraction Strength''': Ranges from zero to 1.{{nt|Needs testing for exact behavior}} | ||
| + | * '''Alpha''': Overall opacity of the TriShape, zero being fully transparent, and one being fully opaque. Can be buggy, so use an alpha property instead whenever possible. | ||
| + | * '''Emissive Color''': Color of any glow effects. If the shader type is not "Glow Shader," it will make the whole mesh glow. | ||
| + | * '''Emissive Strength''': Multiplier on glow intensity. | ||
| + | * '''UV Scale''' is the scaling size of the UV map. You can right-click on your mesh in the render window and choose textures > UV map and manually edit it, rotate, and scale it. | ||
| − | + | === Default === | |
| + | The default shader is the most commonly used. It is good for most solid objects which do not require any additional shading effects. Shapes using the default shader should have a diffuse texture and combined normal/specular texture. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | === Environment Map === |
| + | [[File:EnvShader1.png|thumb|upright=2|Dwarven armor comparison]] | ||
| + | The environment map shader is also quite common. It provides a method of simulating reflectivity by using a prerendered environment texture as the reflection. This is applied additively to the mesh. It is commonly used for metals, ore, and ice. Shapes using the environment map shader should have diffuse, combined normal/specular, environment, and environment mask textures. The environment mask texture is used to define how strongly the cubemap is blended per texel. The environment map shader is incompatible with glow mapping, so if you have a mesh for which you want to use both effects, you have to split it into parts, or overlay a partially transparent mesh. Be sure the Environment Map shader flag is set, and the Glow Map shader flag is ''not'' set. | ||
| − | * | + | Values: |
| − | + | * '''Environment Map Scale''': Multiplier on environment map intensity. Values between 0.25 and 2 are typical. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Glow Shader === | |
| − | === | + | === Parallax === |
| − | + | === Face Tint === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | === Skin Tint === | |
| − | |||
| − | + | === Hair Tint === | |
| − | + | === Multilayer Parallax === | |
| − | |||
| − | + | === Eye Envmap === | |
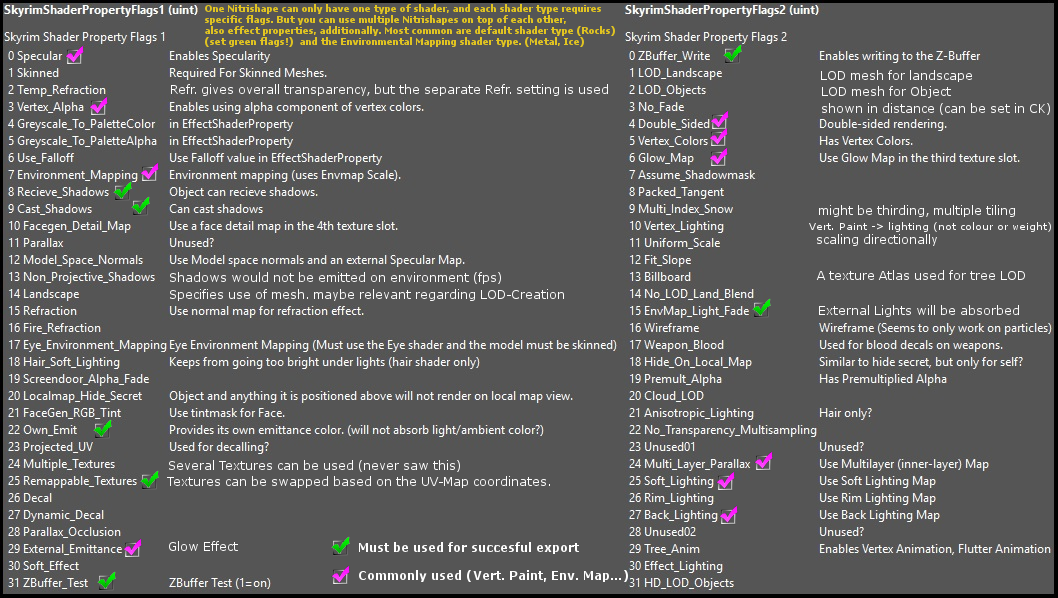
| − | == | + | == Shader Flags == |
| − | + | [[File:BSshadersFlagsExport.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 20:53, 30 November 2025
The BSLightingShaderProperty is the most common type of shader property used in Skyrim. It defines the attributes of the material which is used for shading the mesh. It is suitable for most tangible objects. For objects which require more elaborate blending effects, a BSEffectShaderProperty may be better.
Contents
Shader Types
There are several overall shader types which you can choose from. They are ordered here and in NifSkope generally from most common to least common. Each one uses the textures in its child block BSTextureSet slightly differently. Some of the data which is used in common across different shader types is outlined below:
- Glossiness: Inverse width of the specular highlight. Higher values are narrower, lower values are wider.
- Specular Color: The color of the specular highlight.
- Specular Strength: Multiplier on specular highlight intensity. Values between 0.25 and 1 are typical.
- Refraction Strength: Ranges from zero to 1.Template:Nt
- Alpha: Overall opacity of the TriShape, zero being fully transparent, and one being fully opaque. Can be buggy, so use an alpha property instead whenever possible.
- Emissive Color: Color of any glow effects. If the shader type is not "Glow Shader," it will make the whole mesh glow.
- Emissive Strength: Multiplier on glow intensity.
- UV Scale is the scaling size of the UV map. You can right-click on your mesh in the render window and choose textures > UV map and manually edit it, rotate, and scale it.
Default
The default shader is the most commonly used. It is good for most solid objects which do not require any additional shading effects. Shapes using the default shader should have a diffuse texture and combined normal/specular texture.
Environment Map
The environment map shader is also quite common. It provides a method of simulating reflectivity by using a prerendered environment texture as the reflection. This is applied additively to the mesh. It is commonly used for metals, ore, and ice. Shapes using the environment map shader should have diffuse, combined normal/specular, environment, and environment mask textures. The environment mask texture is used to define how strongly the cubemap is blended per texel. The environment map shader is incompatible with glow mapping, so if you have a mesh for which you want to use both effects, you have to split it into parts, or overlay a partially transparent mesh. Be sure the Environment Map shader flag is set, and the Glow Map shader flag is not set.
Values:
- Environment Map Scale: Multiplier on environment map intensity. Values between 0.25 and 2 are typical.