Difference between revisions of "Arcane University:NetImmerse Format"
(→Texture Slots: shader type link) |
m (→Collision: bypass redirect) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{trail | + | {{trail|Nif implementation}} |
'''NIF''' stands for "'''NetImmerse Format'''," which is a file type that was created for the NetImmerse engine in 1997. This later morphed into the Gamebryo Engine (used for Morrowind, Oblivion, and Fallout 3), which in turn was the basis for the Creation Engine, used by games such as Skyrim, Fallout 4, and Fallout 76. Much more than simple 3D mesh files, Nifs can also contain complex shader and texturing information, as well as character rigs, animations, collison meshes, physics properties, and other information that is passed to the game engine. This article details the structure and workings of Nif files as they are used for Skyrim. | '''NIF''' stands for "'''NetImmerse Format'''," which is a file type that was created for the NetImmerse engine in 1997. This later morphed into the Gamebryo Engine (used for Morrowind, Oblivion, and Fallout 3), which in turn was the basis for the Creation Engine, used by games such as Skyrim, Fallout 4, and Fallout 76. Much more than simple 3D mesh files, Nifs can also contain complex shader and texturing information, as well as character rigs, animations, collison meshes, physics properties, and other information that is passed to the game engine. This article details the structure and workings of Nif files as they are used for Skyrim. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
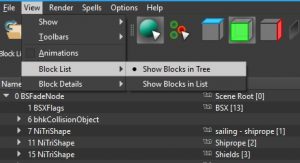
Nifs are organized into blocks or nodes arranged in a hierarchy or "tree." Each block has various properties that define how it functions in the game. | Nifs are organized into blocks or nodes arranged in a hierarchy or "tree." Each block has various properties that define how it functions in the game. | ||
| − | The root node always has a block ID of 0. It is most commonly a BSFadeNode (static bodies), a NiNode (skinned rigged meshes like armors), or a BSLeafAnim/tree node (plants). The root node will usually have attached [[#Metadata|metadata]] blocks that activate other nif properties like animation, Havok physics, and inventory display. 3D Meshes are represented by [[#TriShapes|TriShapes]]. The surface material is defined by a [[#Shader | + | The root node always has a block ID of 0. It is most commonly a BSFadeNode (static bodies), a NiNode (skinned rigged meshes like armors), or a BSLeafAnim/tree node (plants). The root node will usually have attached [[#Metadata|metadata]] blocks that activate other nif properties like animation, Havok physics, and inventory display. 3D Meshes are represented by [[#TriShapes|TriShapes]]. The surface material is defined by a [[#Shader properties|shader property]] block, either a Lighting Shader or an Effect Shader. Animations are defined in Controller blocks, or in child nodes of the shader property. |
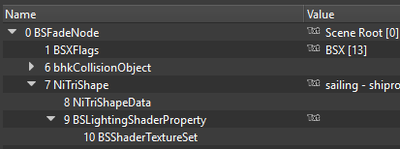
== TriShapes == | == TriShapes == | ||
| + | TriShapes are what contain the mesh data, like vertices, normals, tangents, UV map, and vertex colors. | ||
| + | |||
A NiTriShape can have the following child properties among others: | A NiTriShape can have the following child properties among others: | ||
* '''NiTriShapeData:''' the actual mesh data (vertices, normals, tangents, UV map). | * '''NiTriShapeData:''' the actual mesh data (vertices, normals, tangents, UV map). | ||
| − | * '''[[#Shader | + | * '''[[#Shader properties|Shader property]]''' (BSLightingShaderProperty or BSEffectShaderProperty): holds lighting and texture information. |
* '''[[#Transparency|NiAlphaProperty]]:''' tells the game how to handle transparency in the mesh, if any. | * '''[[#Transparency|NiAlphaProperty]]:''' tells the game how to handle transparency in the mesh, if any. | ||
* '''BSDismemberSkinInstance:''' only present in skinned meshes like armor. It contains the vertex weighting to handle limbs being dismembered from the base mesh, and deform during animation. | * '''BSDismemberSkinInstance:''' only present in skinned meshes like armor. It contains the vertex weighting to handle limbs being dismembered from the base mesh, and deform during animation. | ||
| − | '''BSTriShapes''', used in Skyrim Special Edition, combine the NiTriShape and | + | '''BSTriShapes''', used in Skyrim Special Edition, combine the NiTriShape and NiTriShapeData into a single block. They are not widely supported by nif import and export tools, and cannot be manipulated as easily within NifSkope. They can be converted back and forth by nif converter tools like Cathedral Assets Optimizer or SSE Nif Optimizer. However, LE nifs work fine in Special Edition, and do not need to be converted. In fact, SSE nifs use less precise values, so LE nifs are recommended regardless of which version of the game you are modding. |
| + | |||
| + | '''BSLODTriShapes''' are the same as NiTriShapes, except that they fade out some distance away. This is used in LE to make small details on architecture nifs fade out ''before'' it is replaced with an LOD model. This block has no effect in SSE (no parts fade out individually). | ||
| − | ' | + | == Shader properties == |
| + | Each TriShape defines a set of mesh data. The material data which is used for shading each mesh is contained in a shader property, which is linked in the TriShape's "Shader Property" field. The two most common shader property types in Skyrim are the [[AU:NetImmerse Format/BSLightingShaderProperty|BSLightingShaderProperty]], and the [[AU:NetImmerse Format/BSEffectShaderProperty|BSEffectShaderProperty]]. Lighting shaders are used for most tangible objects, while effect shaders are used for things like magic effects, and some ambient effects like mist or water. Refer to the pages linked above for more detailed information about each type of shader property. | ||
| − | ==Texture | + | ==Texture slots== |
| − | + | {{main|[[AU:NetImmerse Format/Texture Slots]]}} | |
| − | All textures used by Skyrim are [[AU:DDS Data Format|DDS]] (Direct Draw Surface) files (with a few exceptions, such as menu art). | + | All textures used by Skyrim are [[AU:DDS Data Format|DDS]] (Direct Draw Surface) files (with a few exceptions, such as menu art). In a lighting shader, these textures are typically referenced in the <code>BSShaderTextureSet</code> block. In an effect shader, they are contained directly in the shader property itself (and therefore do not follow these texture slot assignments). |
| − | Some slots are reused for multiple different purposes. For example, when a mesh uses the Glow shader, slot | + | Some slots are reused for multiple different purposes. For example, when a mesh uses the Glow shader, slot 2 is used as an emissive map. But when a mesh uses the Skin shader, the same slot is used for skin tint. Be sure to select the proper [[#Shader properties|shader type]], and activate the desired shader flags, for your model to be displayed correctly. It is also important to note that these are in nif order. In the CK [https://ck.uesp.net/wiki/TextureSet TextureSet] records, the order of the slots is different, but they are named. |
Textures are applied based on the [[AU:UV Unwrapping|UV map]] created during 3D modeling. Following [https://www.notion.so/UV-Mapping-Best-Practices-eefa3731217c4c65a907d1990939974f UV Mapping Best Practices] will help to prevent errors in your model. | Textures are applied based on the [[AU:UV Unwrapping|UV map]] created during 3D modeling. Following [https://www.notion.so/UV-Mapping-Best-Practices-eefa3731217c4c65a907d1990939974f UV Mapping Best Practices] will help to prevent errors in your model. | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" style="clear:both; width: | + | {| class="wikitable" style="clear:both; width:90%; margin:1em auto" |
|+ Texture Slots Overview | |+ Texture Slots Overview | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! Texture Slot !! Name !! RGB Channel !! Alpha Channel !! Texture Suffix !! Suggested [https://www.reedbeta.com/blog/understanding-bcn-texture-compression-formats/ Compression] !! Suggested creation method | + | ! Texture Slot !! Name in Creation Kit !! RGB Channel !! Alpha Channel !! Texture Suffix !! Suggested [https://www.reedbeta.com/blog/understanding-bcn-texture-compression-formats/ Compression] !! Suggested creation method |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 0 || Diffuse || Diffuse (base color and ambient occlusion) || (optional) opacity map || (no suffix) || BC1 (no Alpha), BC7<sup>[[#Texture Slot Notes|[a]]]</sup> for RGBA || Base Color and baked AO |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1 || Normal/Gloss || Normal map || Grayscale specular map || _n || BC7<sup>[[#Texture Slot Notes|[a]]]</sup> || RGB normal map. For specular in the alpha channel, invert a roughness map or insert a PBR specularity. Black is zero reflection, white full. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2 || Glow || Glow map / Skin Tint || none || _g / _sk.dds || BC1 || Color glow map or skin tint. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 3 || Height || Grayscale height or parallax{{tn|Does the game read only the first channel, or the average of all three?}} || none || _p || BC4<sup>[[##Texture Slot Notes|[b]]]</sup> || Used for height in parallax shader (broken in vanilla Skyrim). |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 4 || Environment || Cubemap || none || _e || BC1 || Cube projection of environment for simulating reflections. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 5 || Environment Mask || Environment mask || none || _m or _em || BC4<sup>[[##Texture Slot Notes|[b]]]</sup> || Environment mask. Black is no reflection, and white is full intensity reflection (refer to SLOT 4 for environment). |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 6 || Multilayer || Inner layer diffuse || Inner layer diffuse || _i || BC7<sup>[[##Texture Slot Notes|[a]]]</sup> || Color map for inner layer of multilayer parallax shader. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 7 || Backlight mask || Backlight mask / Subsurface tint / Alternate specular || none || _b or _bl / (none) / _s || BC1 || Primarily for back lighting shader. Also used for subsurface tint of multilayer parallax, and specular when using model space normals. |
|} | |} | ||
| − | <div id="Notes" style="font-size:89%; text-align:center"> | + | <div id="Texture Slot Notes" style="font-size:89%; text-align:center"> |
: <small>[a]</small> - BC7 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC3 here. | : <small>[a]</small> - BC7 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC3 here. | ||
: <small>[b]</small> - BC4 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC1 here. | : <small>[b]</small> - BC4 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC1 here. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | == | + | == Collision == |
| − | + | {{main|[[Arcane University:Collision]]}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Collision meshes are used to make objects solid in the Creation Engine. A nif can have a single collision mesh, or many. They can be static or moving. The collision settings are also what make the object affected by physics. They determine what parts of an object are interactable. They are typically simpler than the visible meshes, being made up of fewer vertices, since they are invisible and do not need small detail. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Transparency == | == Transparency == | ||
| − | Transparency is enabled for each NiTriShape by adding a NiAlphaProperty node. | + | Transparency is enabled for each NiTriShape by adding a NiAlphaProperty node. Transparency data is taken from the alpha channel of the diffuse, as well as the alpha channel of the vertex colors, if they exist, even if neither the <code>Vertex Colors</code> nor <code>Vertex Alpha</code> shader flags are enabled. Watch out for this! |
=== Blending === | === Blending === | ||
| − | If | + | {{Note|float=right|max-width=40%|Sometimes when using alpha blending (maybe always), the mesh will not receive shadows correctly. To remedy this, add the <code>Assume_Shadowmask</code> shader flag.}} |
| + | If translucence is desired, "Enable Blending" must be checked. | ||
*For Alpha Blending: | *For Alpha Blending: | ||
| Line 256: | Line 85: | ||
=== Alpha Testing === | === Alpha Testing === | ||
| − | For Alpha Testing, check "Enable Testing." The Alpha Test Function sets how | + | For Alpha Testing, check "Enable Testing." The Alpha Test Function sets how opacity channel grey values (0 to 255 or black to white) will be compared to the Alpha Test Threshold value to determine the threshold at which pixels with partial opacity should be rendered as completely transparent. |
| − | This setting can also be modified at the CK object reference level, allowing a single nif to have variable levels of | + | This setting can also be modified at the CK object reference level, allowing a single nif to have variable levels of opacity. This is used most often in Skyrim to create objects with varying levels of decay, like rugs in Nordic Tombs. |
:Less or Equal: Lighter will be more transparent | :Less or Equal: Lighter will be more transparent | ||
| Line 284: | Line 113: | ||
* Dst Alpha: multiply by value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel | * Dst Alpha: multiply by value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel | ||
* Inv Dst Alpha: multiply by inverse value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel | * Inv Dst Alpha: multiply by inverse value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Metadata== | ==Metadata== | ||
===<span id="BSXFlags node"></span>BSXFlags=== | ===<span id="BSXFlags node"></span>BSXFlags=== | ||
| − | The BSXFlags node goes | + | The BSXFlags node goes in the Extra Data of the root node of the nif. It contains a [[wikipedia:bit field|bit field]] of flags that activate different properties of the object in Skyrim. These properties can be accessed and selected by clicking the small flag icon. The list of flags is as follows: |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! Bit/Number !! Name !! Description | ! Bit/Number !! Name !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 0 (1) || Animated || | + | | Bit 0 (1) || Animated || Has Gamebryo animation |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 1 (2) || Havok || | + | | Bit 1 (2) || Havok || Has Havok collision |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 2 (4) || Ragdoll || | + | | Bit 2 (4) || Ragdoll || Has Havok ragdoll (actor skeleton) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 3 (8) || Complex || Has more than one bhkCollisionObject | + | | Bit 3 (8) || Complex<sup>[[##BSXFlags Notes|[a]]]</sup> || Has more than one bhkCollisionObject |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 4 (16) || Addon || | + | | Bit 4 (16) || Addon || Has addon node(s) (e.g. candle flame) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 5 (32) || Editor marker || | + | | Bit 5 (32) || Editor marker || Has editor markers shown in Creation Kit |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 6 (64) || Dynamic || | + | | Bit 6 (64) || Dynamic || Has Havok dynamic rigid body physics (affected by gravity, can move around) |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 7 (128) || Articulated || Has a single bhkCollisionObject, or a single kinematic chain | + | | Bit 7 (128) || Articulated<sup>[[##BSXFlags Notes|[a]]]</sup> || Has a single bhkCollisionObject, or a single kinematic chain. This is influenced by a NiSwitchNode, if one is present. Even if multiple branches of the switch node have collision, if a single collision object or kinematic chain is to be displayed at a time, this bit will be set. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 8 (256) || Needs transform updates || Never | + | | Bit 8 (256) || Needs transform updates || Unknown use. Never set in vanilla Skyrim or DLCs |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Bit 9 (512) || External emit || | + | | Bit 9 (512) || External emit || Has shapes which use external emittance (e.g. glow that is set dynamically, like windows that change glow color based on weather region) |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | <div id="BSXFlags Notes" style="font-size:89%; text-align:center"> | |
| − | + | : <small>[a]</small> - Bits 3 (Complex) and 7 (Articulated) appear to only be used by vanilla Skyrim for grabbing items. Despite this, they are typically set based on their descriptions here for all objects regardless of whether they may be grabbed. | |
| + | </div> | ||
This is a cheat sheet of some common BSXFlags values used in vanilla objects: | This is a cheat sheet of some common BSXFlags values used in vanilla objects: | ||
| Line 347: | Line 150: | ||
| 130 || Statics || The player won't be able to interact with the object aside from colliding with it, e.g. Tables, fireplaces, rocks | | 130 || Statics || The player won't be able to interact with the object aside from colliding with it, e.g. Tables, fireplaces, rocks | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 131 || Animated | + | | 131 || Animated objects || Animated objects like doors or chests with single collision objects or single kinematic chains. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 11 || Animated objects || Animated objects like doors or chests with multiple collision objects or kinematic chains. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 194 || Clutter || Havok is activated on these objects, meaning that they have physics applied, e.g. Clutter, weapons, armor ground items | + | | 194 || Clutter/Misc || Dynamic Havok is activated on these objects, meaning that they have physics applied, e.g. Clutter, weapons, armor ground items |
|} | |} | ||
=== Inventory Marker === | === Inventory Marker === | ||
| − | |||
The inventory marker (BSInvMarker) block determines the rotation and zoom of an item when viewed in the inventory. Rotation X, Y and Z specify the clockwise rotation in ''radians*1000'' around that axis, when viewed from the positive side of that axis. The standard view (no rotations) in the inventory is viewing from the positive Y axis. Increasing the zoom value makes the item appear larger in the inventory, decreasing it makes it smaller. | The inventory marker (BSInvMarker) block determines the rotation and zoom of an item when viewed in the inventory. Rotation X, Y and Z specify the clockwise rotation in ''radians*1000'' around that axis, when viewed from the positive side of that axis. The standard view (no rotations) in the inventory is viewing from the positive Y axis. Increasing the zoom value makes the item appear larger in the inventory, decreasing it makes it smaller. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[AU:Nif Implementation|Nif Implementation]]: Tutorials on making nifs work in Skyrim. | * [[AU:Nif Implementation|Nif Implementation]]: Tutorials on making nifs work in Skyrim. | ||
* [[Arcane_University:DDS_Data_Format|DDS Data Format]]: Information on the DDS format, used for textures. | * [[Arcane_University:DDS_Data_Format|DDS Data Format]]: Information on the DDS format, used for textures. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Data_Format]] | [[Category:Data_Format]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 1 December 2025
NIF stands for "NetImmerse Format," which is a file type that was created for the NetImmerse engine in 1997. This later morphed into the Gamebryo Engine (used for Morrowind, Oblivion, and Fallout 3), which in turn was the basis for the Creation Engine, used by games such as Skyrim, Fallout 4, and Fallout 76. Much more than simple 3D mesh files, Nifs can also contain complex shader and texturing information, as well as character rigs, animations, collison meshes, physics properties, and other information that is passed to the game engine. This article details the structure and workings of Nif files as they are used for Skyrim.
Contents
General NIF structure[edit]
Nifs are organized into blocks or nodes arranged in a hierarchy or "tree." Each block has various properties that define how it functions in the game.
The root node always has a block ID of 0. It is most commonly a BSFadeNode (static bodies), a NiNode (skinned rigged meshes like armors), or a BSLeafAnim/tree node (plants). The root node will usually have attached metadata blocks that activate other nif properties like animation, Havok physics, and inventory display. 3D Meshes are represented by TriShapes. The surface material is defined by a shader property block, either a Lighting Shader or an Effect Shader. Animations are defined in Controller blocks, or in child nodes of the shader property.
TriShapes[edit]
TriShapes are what contain the mesh data, like vertices, normals, tangents, UV map, and vertex colors.
A NiTriShape can have the following child properties among others:
- NiTriShapeData: the actual mesh data (vertices, normals, tangents, UV map).
- Shader property (BSLightingShaderProperty or BSEffectShaderProperty): holds lighting and texture information.
- NiAlphaProperty: tells the game how to handle transparency in the mesh, if any.
- BSDismemberSkinInstance: only present in skinned meshes like armor. It contains the vertex weighting to handle limbs being dismembered from the base mesh, and deform during animation.
BSTriShapes, used in Skyrim Special Edition, combine the NiTriShape and NiTriShapeData into a single block. They are not widely supported by nif import and export tools, and cannot be manipulated as easily within NifSkope. They can be converted back and forth by nif converter tools like Cathedral Assets Optimizer or SSE Nif Optimizer. However, LE nifs work fine in Special Edition, and do not need to be converted. In fact, SSE nifs use less precise values, so LE nifs are recommended regardless of which version of the game you are modding.
BSLODTriShapes are the same as NiTriShapes, except that they fade out some distance away. This is used in LE to make small details on architecture nifs fade out before it is replaced with an LOD model. This block has no effect in SSE (no parts fade out individually).
Shader properties[edit]
Each TriShape defines a set of mesh data. The material data which is used for shading each mesh is contained in a shader property, which is linked in the TriShape's "Shader Property" field. The two most common shader property types in Skyrim are the BSLightingShaderProperty, and the BSEffectShaderProperty. Lighting shaders are used for most tangible objects, while effect shaders are used for things like magic effects, and some ambient effects like mist or water. Refer to the pages linked above for more detailed information about each type of shader property.
Texture slots[edit]
- Main article: AU:NetImmerse Format/Texture Slots
All textures used by Skyrim are DDS (Direct Draw Surface) files (with a few exceptions, such as menu art). In a lighting shader, these textures are typically referenced in the BSShaderTextureSet block. In an effect shader, they are contained directly in the shader property itself (and therefore do not follow these texture slot assignments).
Some slots are reused for multiple different purposes. For example, when a mesh uses the Glow shader, slot 2 is used as an emissive map. But when a mesh uses the Skin shader, the same slot is used for skin tint. Be sure to select the proper shader type, and activate the desired shader flags, for your model to be displayed correctly. It is also important to note that these are in nif order. In the CK TextureSet records, the order of the slots is different, but they are named.
Textures are applied based on the UV map created during 3D modeling. Following UV Mapping Best Practices will help to prevent errors in your model.
| Texture Slot | Name in Creation Kit | RGB Channel | Alpha Channel | Texture Suffix | Suggested Compression | Suggested creation method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Diffuse | Diffuse (base color and ambient occlusion) | (optional) opacity map | (no suffix) | BC1 (no Alpha), BC7[a] for RGBA | Base Color and baked AO |
| 1 | Normal/Gloss | Normal map | Grayscale specular map | _n | BC7[a] | RGB normal map. For specular in the alpha channel, invert a roughness map or insert a PBR specularity. Black is zero reflection, white full. |
| 2 | Glow | Glow map / Skin Tint | none | _g / _sk.dds | BC1 | Color glow map or skin tint. |
| 3 | Height | Grayscale height or parallaxtesting needed | none | _p | BC4[b] | Used for height in parallax shader (broken in vanilla Skyrim). |
| 4 | Environment | Cubemap | none | _e | BC1 | Cube projection of environment for simulating reflections. |
| 5 | Environment Mask | Environment mask | none | _m or _em | BC4[b] | Environment mask. Black is no reflection, and white is full intensity reflection (refer to SLOT 4 for environment). |
| 6 | Multilayer | Inner layer diffuse | Inner layer diffuse | _i | BC7[a] | Color map for inner layer of multilayer parallax shader. |
| 7 | Backlight mask | Backlight mask / Subsurface tint / Alternate specular | none | _b or _bl / (none) / _s | BC1 | Primarily for back lighting shader. Also used for subsurface tint of multilayer parallax, and specular when using model space normals. |
- [a] - BC7 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC3 here.
- [b] - BC4 is not supported by Oldrim/LE. If modding for LE, use BC1 here.
Collision[edit]
- Main article: Arcane University:Collision
Collision meshes are used to make objects solid in the Creation Engine. A nif can have a single collision mesh, or many. They can be static or moving. The collision settings are also what make the object affected by physics. They determine what parts of an object are interactable. They are typically simpler than the visible meshes, being made up of fewer vertices, since they are invisible and do not need small detail.
Transparency[edit]
Transparency is enabled for each NiTriShape by adding a NiAlphaProperty node. Transparency data is taken from the alpha channel of the diffuse, as well as the alpha channel of the vertex colors, if they exist, even if neither the Vertex Colors nor Vertex Alpha shader flags are enabled. Watch out for this!
Blending[edit]
NOTE: Sometimes when using alpha blending (maybe always), the mesh will not receive shadows correctly. To remedy this, add the Assume_Shadowmask shader flag.
|
If translucence is desired, "Enable Blending" must be checked.
- For Alpha Blending:
- Source Blend Mode: Src Alpha
- Destination Blend Mode: Inv Src Alpha
- For Additive Blending:
- Source Blend Mode: One
- Destination Blend Mode: One
- For Multiplicative Blending:
- Source Blend Mode: Zero
- Destination Blend Mode: Src Color
- For 2x Multiplicative Blending:
- Source Blend Mode: Dst Color
- Destination Blend Mode: Src Color
Alpha Testing[edit]
For Alpha Testing, check "Enable Testing." The Alpha Test Function sets how opacity channel grey values (0 to 255 or black to white) will be compared to the Alpha Test Threshold value to determine the threshold at which pixels with partial opacity should be rendered as completely transparent.
This setting can also be modified at the CK object reference level, allowing a single nif to have variable levels of opacity. This is used most often in Skyrim to create objects with varying levels of decay, like rugs in Nordic Tombs.
- Less or Equal: Lighter will be more transparent
- Greater or Equal: Darker will be more transparent
- Alpha Test Threshold: Value from 0 to 255 (black to white)
Color Blending[edit]
Color Blending Equation
- (Source * SourceBlendMode) + (Destination * DestinationBlendMode)
"Source" is the color of the model materials in that pixel before blending. "Destination" is the color of what is behind the model in that same pixel before blending. These two values are modified by the value of the blend mode in that same pixel, then they are added together.
Blend Modes (a.k.a. Blend Factor)
- One: multiply by one (no modification)
- Zero: multiply by zero
- Src Color: multiply by “Source”
- Inv Src Color: multiply by inverse “Source”
- Dst Color: multiply by “Destination”
- Inv Dst Color: multiply by inverse “Destination”
- Src Alpha: multiply by value of the model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel
- Inv Src Alpha: multiply by inverse value of the model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel
- Dst Alpha: multiply by value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel
- Inv Dst Alpha: multiply by inverse value of the background model’s alpha channel (diffuse and vertex colors) present at that pixel
Metadata[edit]
BSXFlags[edit]
The BSXFlags node goes in the Extra Data of the root node of the nif. It contains a bit field of flags that activate different properties of the object in Skyrim. These properties can be accessed and selected by clicking the small flag icon. The list of flags is as follows:
| Bit/Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bit 0 (1) | Animated | Has Gamebryo animation |
| Bit 1 (2) | Havok | Has Havok collision |
| Bit 2 (4) | Ragdoll | Has Havok ragdoll (actor skeleton) |
| Bit 3 (8) | Complex[a] | Has more than one bhkCollisionObject |
| Bit 4 (16) | Addon | Has addon node(s) (e.g. candle flame) |
| Bit 5 (32) | Editor marker | Has editor markers shown in Creation Kit |
| Bit 6 (64) | Dynamic | Has Havok dynamic rigid body physics (affected by gravity, can move around) |
| Bit 7 (128) | Articulated[a] | Has a single bhkCollisionObject, or a single kinematic chain. This is influenced by a NiSwitchNode, if one is present. Even if multiple branches of the switch node have collision, if a single collision object or kinematic chain is to be displayed at a time, this bit will be set. |
| Bit 8 (256) | Needs transform updates | Unknown use. Never set in vanilla Skyrim or DLCs |
| Bit 9 (512) | External emit | Has shapes which use external emittance (e.g. glow that is set dynamically, like windows that change glow color based on weather region) |
- [a] - Bits 3 (Complex) and 7 (Articulated) appear to only be used by vanilla Skyrim for grabbing items. Despite this, they are typically set based on their descriptions here for all objects regardless of whether they may be grabbed.
This is a cheat sheet of some common BSXFlags values used in vanilla objects:
| Number | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 130 | Statics | The player won't be able to interact with the object aside from colliding with it, e.g. Tables, fireplaces, rocks |
| 131 | Animated objects | Animated objects like doors or chests with single collision objects or single kinematic chains. |
| 11 | Animated objects | Animated objects like doors or chests with multiple collision objects or kinematic chains. |
| 194 | Clutter/Misc | Dynamic Havok is activated on these objects, meaning that they have physics applied, e.g. Clutter, weapons, armor ground items |
Inventory Marker[edit]
The inventory marker (BSInvMarker) block determines the rotation and zoom of an item when viewed in the inventory. Rotation X, Y and Z specify the clockwise rotation in radians*1000 around that axis, when viewed from the positive side of that axis. The standard view (no rotations) in the inventory is viewing from the positive Y axis. Increasing the zoom value makes the item appear larger in the inventory, decreasing it makes it smaller.
See Also[edit]
- Nif Implementation: Tutorials on making nifs work in Skyrim.
- DDS Data Format: Information on the DDS format, used for textures.